Learning objective
- To explore the block code features of MakeCode.
Success criteria
- I can identify different blocks in MakeCode.
- I can describe what coding blocks do.
- I can create a sequence of instructions.
National curriculum
Computing
Pupils should be taught to:
- Understand what algorithms are; how they are implemented as programs on digital devices; and that programs execute by following precise and unambiguous instructions.
- Use logical reasoning to predict the behaviour of simple programs.
- Recognise common uses of information technology beyond school.
Cross-curricular links
None.
Before the lesson
Check all images, videos, links and presentation slides are suitable for your class.
- Presentation: Brain dump.
- Presentation: Action cards.
- Presentation: Block hunt.
- Devices (one each).
- Link: Microsoft MakeCode.*
- Link: How to code with Microsoft MakeCode on VideoLink (optional – see Adaptive teaching).*
*These are external websites and we do not have control over their content – please check before showing them to the children.
Print in advance of the lesson.
Subject knowledge
On start block
- It contains code that runs once when the program begins.
- Consider this block as setting up everything the micro:bit requires before it begins its main tasks.
- For example, place an instruction inside the ‘on start’ block to display a name when the micro:bit turns on.
Forever block
- It contains code that runs continuously in a loop as long as the micro:bit is on.
- This block is used for actions that need to be repeated, such as flashing lights or checking for button presses.
- For example, to have the micro:bit repeatedly displaying a pattern of lights, place those instructions inside the ‘forever’ block.
These blocks help organise the code: ‘on start’ for one-time setup tasks and ‘forever’ for ongoing, repeated actions.
Lesson organisation
Using a desktop
Open a web browser and follow the link: Microsoft MakeCode to access it on a desktop.
Using a tablet
Open the link Microsoft MakeCode in a tablet browser or use one of the following links to install the app.
- Link: MakeCode - Apple App Store.*
- Link: MakeCode - Google Play.*
*These links have been selected for the teacher only and are not intended to be shown to pupils.
Computational thinking vocabulary
At this stage, the children do not need to learn the terms decomposition, abstraction, pattern recognition and algorithm design so these words are not included in the vocabulary section of the lesson plan. Mentioning them when teaching computational thinking skills may be helpful.
Lesson plan
1: Recap and recall
Display the Presentation: Brain dump and arrange the children into pairs.
Presentation: Brain dump
Allow time for paired discussion before inviting the children to share their ideas.
The children may recall:
- Block coding uses blocks to create a sequence of instructions for a computer.
- Blocks can make something move forward, left or right.
- Blocks are dragged and dropped.
- The order of the blocks is important so that the program works.
2: Attention grabber
Display the Presentation: Action cards.
Presentation: Action cards
Invite a child to come up and select a card, then drag it to the sequencing area of the screen.
Repeat, asking different children to select and add a card to the sequence each time. Encourage them to consider the order and how each action affects the next; for example, sitting down and jumping might be tricky.
Review the commands with the children and perform the actions together as a class once the sequence is complete. Repeat to create a new sequence if time allows.
Point out that following the commands in the sequence is similar to programming a computer or device as it involves giving instructions to make the computer perform specific tasks.
- How well did the sequence work?
- Were there any actions in a place where they did not make sense?
3: Main event
Watch the Pupil video: Introduction to MakeCode.
Pupil video: Introduction to MakeCode
Discuss any key findings that the children have found from the video.
Open the link: Microsoft MakeCode and introduce the children to the platform. Allow the children to hold and pass a micro:bit round if a physical one is available.
Remind the children that in the last lesson, they used a skill to break down a problem into smaller pieces and also focused on the important parts of the program. Explain that today, when using MakeCode, they will focus on recognising different patterns (pattern recognition) and creating an algorithm (algorithm design).
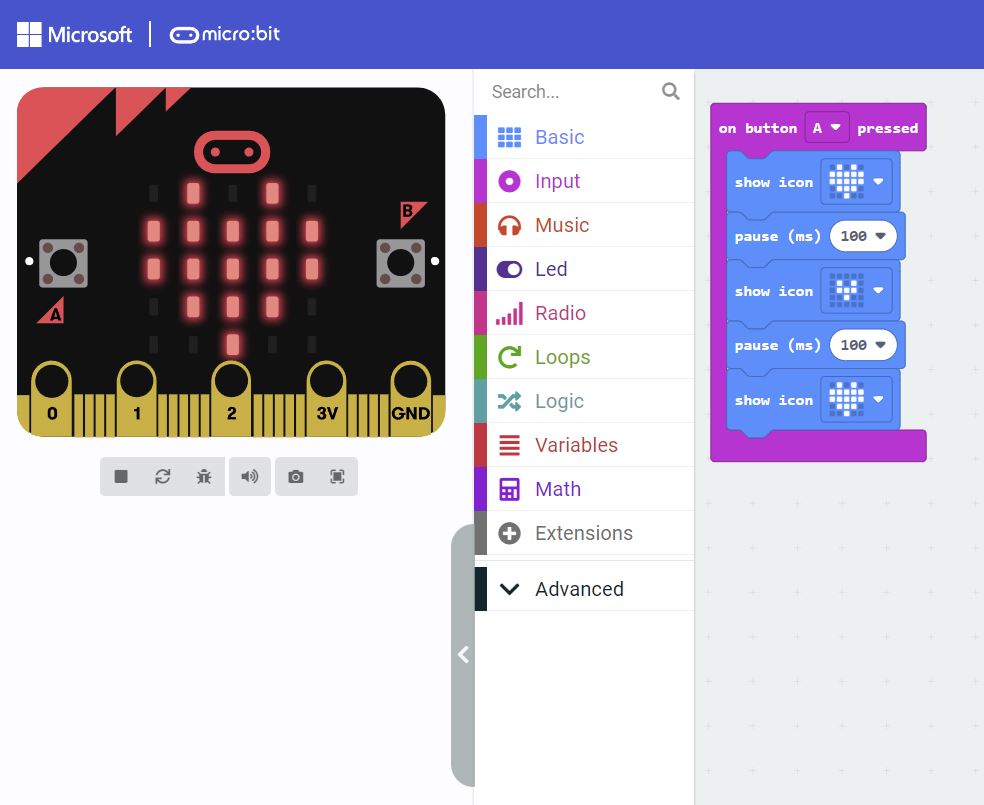
Inform them that each block is an instruction that tells the micro:bit what to do. Point out that a program is just a series of these instructions, or algorithms, that the micro:bit follows to perform tasks.
Without giving any more information, allow the children time to explore the platform independently.
Show the children the Activity: Block hunt, and explain that they will tinker with MakeCode to discover what the different blocks do.
Hand out the devices (one each) and share the link: Microsoft MakeCode with the children. Hand out the Activity: Block hunt (one each) and encourage the children to click around to identify and discover what the different blocks do.
Invite the class to share their initial thoughts and observations, noting any interesting findings they may share. Use the Resource: Block hunt (one teacher copy) to support.
Inform the children that they will use the ‘input’ and ‘basic’ blocks in MakeCode to create a project over the coming weeks. Explain that these blocks are the basic parts needed to make interactive programs; they help us learn how coding tells a computer what to do. Point out that the ‘on start’ and ‘forever’ blocks will already be on the screen. Explain their importance and how they are used (see Teacher knowledge).
Allow the children to continue tinkering, encouraging them to explore the effects of different combinations using the ‘input’ and ‘basic’ categories. While the children are tinkering, walk around the room to answer any questions and gauge what they might need more help with later.
4: Wrapping up
Arrange the children into pairs and ask each child to show their partner one thing they created or discovered in MakeCode. Encourage them to explain what the blocks they used do and how they fit together.
Ask a few pairs to share what they discussed with the class.
Highlight any interesting findings or creative uses of blocks. Reinforce the idea that by creating a sequence of instructions in MakeCode, they made an algorithm and used the skill of algorithm design just like a programmer. Inform the children that by noticing and using repeated blocks, they practised the skill of pattern recognition, which helped them understand how to create better sequences in their programs (e.g. using a block more than once).
Extended-mode explainer videos
How to extend your display to view the lesson page and preseantion mode simultaneously. Choose your operating system below to watch the video
If you need further support with extending your display,
please contact [email protected].
Extended-mode explainer video: For Mac
Extended-mode explainer video: For Windows
Adaptive teaching
Pupils needing support
Could use the Activity: Block hunt: support version to identify a smaller range of blocks and explain what they do verbally; could watch the video How to code with Microsoft MakeCode to introduce them to MakeCode.
Pupils working at greater depth
Should write what each block does using the Activity: Block hunt, giving specific examples (e.g the micro:bit flashed using the ‘show leds’ block).
Assessing progress and understanding
Pupils with secure understanding indicated by: identifying the different blocks and recognising some of their functions; explaining their basic use; creating a simple sequence of instructions using at least three different blocks; recognising that the blocks fit together to form a sequence.
Pupils working at greater depth indicated by: identifying and categorising different blocks and explaining their functions within a program; creating a complex sequence of instructions using multiple blocks; explaining in detail how the blocks form a sequence and recognising how changes to the sequence affect the outcome.
Vocabulary definitions
-
algorithm
A set of steps to solve a problem or complete a task.
-
block coding
Creating code using visual blocks that fit together like a puzzle.
-
coding
Writing instructions that tell a computer what to do.
-
sequence
Putting steps in the correct order.