Learning objective
- To create a working gear system and explain its function.
Success criteria
- I can give examples of mechanical systems that use gears in everyday objects.
- I can describe how gears allow us to increase the output of a mechanism.
- I can make a simple gear.
- I can connect gears in a gear system.
National curriculum
Design and technology
Design
Pupils should be taught to:
- Generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through discussion, annotated sketches, cross-sectional and exploded diagrams, prototypes, pattern pieces and computer-aided design.
Make
Pupils should be taught to:
- Select from and use a wider range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks [for example, cutting, shaping, joining and finishing], accurately.
- Select from and use a wider range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles and ingredients, according to their functional properties and aesthetic qualities.
Evaluate
Pupils should be taught to:
- Evaluate their ideas and products against their own design criteria and consider the views of others to improve their work.
- Understand how key events and individuals in design and technology have helped shape the world.
Technical knowledge
Pupils should be taught to:
- Understand and use mechanical systems in their products [for example, gears, pulleys, cams, levers and linkages].
See National curriculum – Design and technology - Key stages 1 and 2.
Cross-curricular links
Science
Forces
Pupils should be taught to:
- Recognise that some mechanisms, including levers, pulleys and gears, allow a smaller force to have a greater effect.
See National curriculum – Science - Key stages 1 and 2.
Geography
Human and physical geography
Pupils should be taught to:
- Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water.
See National curriculum – Geography key stages 1 and 2.
British values
- Mutual respect.
See Promoting fundamental British values as part of SMSC in schools (non-statutory advice) – contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v2.0.
Before the lesson
Check all images, videos, links and presentation slides are suitable for your class.
- Presentation: Evaluating gears.
- Equipment to make gears (per group – see Main event):
- 1 piece of A4 double-faced corrugated card (see Teacher knowledge);
- 1 long, thin strip of single-faced corrugated card (minimum 2 cm by 24 cm);
- 25 paper clips;
- 1 thumb tack;
- 1 toothpick;
- 1 small ball of modelling dough;
- 1 heavy book;
- 6 normal-length split pins to make handles for the gears (optional);
- 1 glue stick;
- scissors (one each);
- access to quick-drying PVA glue (see Teacher knowledge).
- Equipment to make a gear system mounting board (per group – see Main event):
- 1 piece of A4 double-faced corrugated card (see Teacher knowledge);
- 2 extra-long split pins;
- 1 small ball of sticky tack to make handles for the gears (optional);
- 2 small balls of modelling dough to stand the mounting board upright (optional).
- Link: Assessment – D&T: Y5: Mechanisms: Gears and pulleys (optional – see Attention grabber).
Print in advance of the lesson.
The Knowledge organiser provides a visual summary of the key facts and vocabulary for the unit. The children can use it throughout the unit to check keyword meanings or spellings and to help them remember important information when completing an activity. Find further ideas for using the Knowledge organiser to support adaptive teaching here.
Teacher knowledge
Gears
- A gear is a wheel with teeth.
- A gear system is a set of gears that fit together to change the speed, direction or force of movement.
- Larger gears with more teeth turn slower while smaller gears with fewer teeth turn faster.
- The input is where the force or motion starts and the output is where the force or motion ends after passing through the gears. For example, when pedalling a bicycle (input), the gears turn and make the wheels spin (output).
- Gears transmit power from one part of a machine to another.
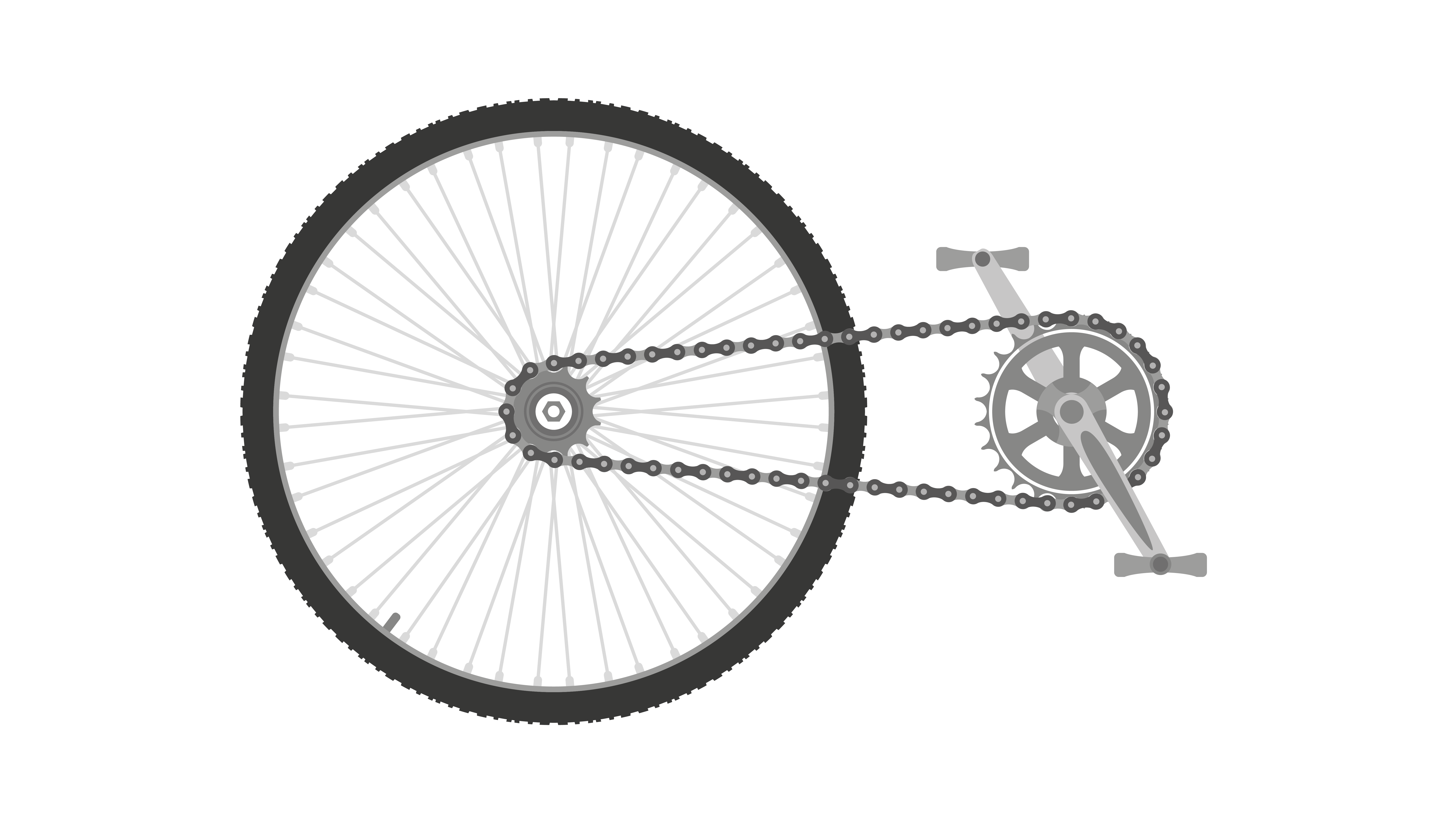
Examples
- Changing gears on a bicycle to make pedalling easier.
- Clocks use gears to control the movement of the hands accurately.
- Car transmissions use gears to adjust the vehicle’s speed.
- Wind turbines use gears to increase the speed of the generator, making it easier to produce electricity from the slower turning blades.
Importance of gears
- Gears make work easier by changing the amount of force needed or the direction of movement. They help machines complete tasks more efficiently.
- These simple machines leverage the basic principles of physics to reduce the effort needed to perform tasks, making everyday activities easier and more efficient.
Cardboard
- Single-faced corrugated cardboard has one smooth side and one ridged side and can be used to create teeth on gears.
- Double-faced corrugated cardboard has two smooth sides with ridges sandwiched between them: this card is used in packaging boxes.
Misconceptions
The children may think that:
- ‘All gears turn at the same speed’ – gears of different sizes or with different numbers of teeth turn at different speeds. Larger gears with more teeth turn slower while smaller gears with fewer teeth turn faster.
- ‘Input and output are always the same’ – the input force or speed applied to a gear is not always the same as the output force or speed. Gears can change the amount of force and speed transferred, increasing or decreasing them based on their design.
- ‘A single gear can be effective’ – a single gear is ineffective because gears need to work in pairs or systems to transfer motion and force from one part of a machine to another. A lone gear cannot perform this function by itself.
Lesson organisation
- Save all gears, gear systems and mounting boards for repeated use throughout the unit.
- Reuse double-faced, corrugated cardboard from boxes and packaging to reduce costs.
Making gears
The groups need to make six gears in total. Each gear requires three layers of card and one set of teeth to be made.
- Groups of two: any children skilled at sticking, using scissors and making could work in pairs, with each partner making one of each type of gear (three gears each).
- Groups of three: the children with some skill could work in groups of three, making one pair of gears each.
- Groups of six: less skilled children could work in groups of six, with each child focussing on making one gear.
Make pots of quick-drying PVA glue accessible to the pupils. Use paint brushes or lolly sticks to spread the glue if the pots do not have a nozzle.
Troubleshooting
- The two circles to create the gears must be stuck together with the template side facing outwards so the dot in the centre can be seen when making a hole for the axle.
- The single-faced corrugated card strips must be cut across the ridges to create teeth not along a single ridge.
The information within this section provides basic generic guidance only and is not tailored to the circumstances of your school or class. You must ensure you refer to and follow your own school’s health & safety policy and complete any necessary risk assessments. It is the teacher’s responsibility to check all resources and lesson content to ensure it is suitable for their class setting.
Health and Safety
Remind the pupils:
- Use the equipment only as instructed by the teacher.
- Handle the scissors with care, cutting away from their fingers.
- Handle the thumb tack and split pins carefully, being careful not to touch the sharp ends.
Lesson plan
1: Recap and recall
Before undergoing this unit, check that the children understand the following:
- A mechanical system can allow something to move more efficiently.
- Mechanical systems have more than one mechanism that moves to make them work.
- Either wheels move around the axle or with the axle.
2: Attention grabber
Optional: provide each child with a copy of the Knowledge catcher (see link: Assessment – D&T: Y5: Mechanisms: Gears and pulleys) and ask them to complete it to the best of their ability. Explain that at the end of the unit, they will revisit it, adding more information in a different colour.
Play the Pupil video: Gears, which introduces gears, how they work in gear systems, their function, some interesting historical examples (including the Antikythera mechanism, medieval tower clocks and Archimedes screw) and some modern examples (including wind turbines).
Pupil video: Gears
Ask the class to discuss with a partner the following questions:
- What is a gear and how does it work? (A gear is a wheel with teeth that fits into another gear’s teeth. They work by turning each other and they can change the speed or direction of movement.)
- Can you explain the terms ‘input’ and ‘output’ in relation to gears? (The input is where the force or motion starts and the output is where the force or motion ends after passing through the gears. For example, when turning a handle (input), the gears turn and can make something else move (output).)
- Why are gears like wind turbines essential in modern technology? (Gears in wind turbines help increase the generator’s speed, making producing electricity from the slower turning blades easier.)
- How do gears make work easier in machines? (Gears make work easier by changing the input movement’s speed, force or direction.)
Take feedback from the class.
3: Main event
Inform the class that they will make gears with different types of teeth and compare and evaluate how well the teeth work.
Play the Pupil video: How to make gears, which shows how to make gears with teeth made from three different materials.
Pupil video: How to make gears
Arrange the class into small groups (see Teacher knowledge for recommended grouping). Provide each group with the Resource: Gears template and the equipment for making gears and a gear system mounting board (see Have ready). Ask a child to roughly cut out the gear pieces and instruct them to distribute them to the group for accurate cutting before making the gears. Note: the pieces the groups need will depend on the group size (see Teacher knowledge).
Allow time for all groups to complete making their gears. Consider playing the Pupil video: How to make gears on repeat without the sound if required:
Making gears with paper clip teeth (0:53 minutes).- Making gears with modelling dough teeth (1:20 minutes).
- Making gears with corrugated teeth (1:48 minutes).
- Making the gear mounting board (2:37 minutes).
4: Wrapping up
Explain that the children will now test, compare and evaluate their gears. Display the Presentation: Evaluating gears, which shows some keywords to consider when comparing and evaluating. Ask the groups to discuss the keywords and suggest questions they could ask to learn more about each one in relation to their gear system.
Presentation: Evaluating gears
Click to reveal the evaluation criteria questions associated with each keyword for the groups to discuss:
- Functionality: do the teeth mesh together, allowing the gears to turn smoothly? (Answers may include yes, the teeth mesh together neatly and the gears cause one another to turn smoothly; no, the teeth are too thin and do not cause each other to turn; no, the teeth are not evenly spaced; no, the teeth are not sturdy enough.)
- Aesthetics: are the gears made neatly and do they look appealing? (Answers may include yes, the gears are cut precisely and look neat; yes, the gears are colourful and attractive; no, the gears are unevenly cut and look messy; no, the gears look plain and unappealing.)
- User experience: are the gears easy to use and assemble? (Answers may include yes, the gears are easy to cut, stick together and turn without much effort; no, the gears are difficult to cut and stick and the teeth are fiddly to make; no, the gears require too much force to turn.)
- Sustainability: are the materials used for the gears environmentally friendly? (Answers may include yes, the gears are made from recycled cardboard and biodegradable materials; yes, the materials are recyclable and have a low environmental impact.)
- Cost: are the gears made from cost-effective materials? (Answers may include yes, the materials used are inexpensive and readily available; yes, the gears were made within budget.)
Instruct the groups to test, compare and evaluate their three types of gears (paper clips, modelling dough and corrugated teeth) by discussing the evaluation criteria questions.
Note: save all gears, gear systems and mounting boards for repeated use throughout the unit.
Extended-mode explainer videos
How to extend your display to view the lesson page and preseantion mode simultaneously. Choose your operating system below to watch the video
If you need further support with extending your display,
please contact [email protected].
Extended-mode explainer video: For Mac
Extended-mode explainer video: For Windows
Adaptive teaching
Pupils needing extra support:
Could use the Knowledge organiser to help support them answer questions on gears; could work in a group of six and focus on making a single gear; should have the Pupil video: How to make gears available for rewatching as they make their gears.
Pupils working at greater depth:
Should work in a pair to create the three pairs of gears, making one of each type of gear; should write down evaluation criteria questions in their book and use these to compare their gears.
Assessing progress and understanding
Pupils with secure understanding indicated by: giving examples of mechanical systems that use gears in everyday objects (e.g. bicycles and clocks); describing how gears allow us to increase the output of a mechanism; making a simple gear; connecting gears in a gear system.
Pupils working at greater depth indicated by: making multiple gears with teeth made from different materials; suggesting evaluation criteria for comparing the different gears; identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the different gears.
Vocabulary definitions
-
force
A push, pull or twist.
-
gear
A wheel with teeth.
-
gear system
A set of gears that fit together to change the speed, direction or force of motion.
-
input
The motion used to start a mechanism.
-
machine
A tool or device that makes work easier by changing the size, speed or direction of a force.
-
mechanism
A system of moving parts.
-
output
The motion that happens as a result of starting the input.

