Energy: Circuits, batteries and switches
Developing knowledge of circuits, the effects of changing voltage and how switches contribute to different devices.
The Curriculum and Assessment Review final report has been released. We’re reviewing the recommendations and planning for future updates. Learn more
- Subjects >
- Science >
- Key stage 2 >
- Year 6 >
-
Energy: Circuits, batteries and switches
Unit outcomes
Pupils who are secure will be able to:
- Describe the function of key electrical components and explain how the models used in the lesson represent these.
- Correctly predict if an electrical circuit will work or not, explaining why using their knowledge of complete loops, power sources and presence of components.
- Describe the relationship between the number of bulbs in a circuit, the bulb brightness and the amount of resistance.
- Explain that increasing the number of components increases the resistance, affecting the flow of current and energy transferred.
- Identify that batteries are a voltage source; they come in different voltages, affecting bulb brightness.
- Describe that voltage can be changed using different numbers of cells in a circuit and that more cells or a higher voltage causes brighter bulbs.
- Use the relationship between voltage and bulbs to predict what will happen with buzzers and motors.
- Build an electrical circuit with a switch to control its function, explain how the switch and the electrical circuit solve the problem and recall different examples of problems that can be solved using an electrical circuit.
When working scientifically, pupils who are secure will be able to:
- Draw circuit diagrams with straight lines and using standard circuit symbols.
- Design a results table with an appropriate number of columns and headings with units.
- Identify the changed, measured and control variables in an enquiry to plan a method.
Please note that Kapow Primary Science lessons are designed to be 1 hour and 30 minutes long to reflect the requirements of a core subject.
Suggested prior learning
Energy: Electricity and circuits
Get startedLessons
Lesson 1: Components and circuits
Knowledge
- To use recognised symbols for electrical components.
Lesson 2: Circuit diagrams
Knowledge
- To predict and present results for electrical circuits.
Working scientifically
- To use standardised symbols when drawing diagrams.
Lesson 3: Current and resistance
Knowledge
- To recognise a link between the number of components and resistance.
Working scientifically
- To explain results using scientific knowledge.
Lesson 4: Batteries and voltage
Knowledge
- To identify ways to change voltage within an electrical circuit.
Working scientifically
- To design a results table.
Lesson 5: Voltage and bulb brightness
Knowledge
- To investigate how voltage affects bulb brightness.
Working scientifically
- To plan an enquiry.
Lesson 6: Practical circuits
Knowledge
- To apply knowledge of circuits and components to a practical solution.
Science in action
- To recognise that scientific knowledge can solve a problem.
Key skills
Key knowledge
Related content
Unit resources
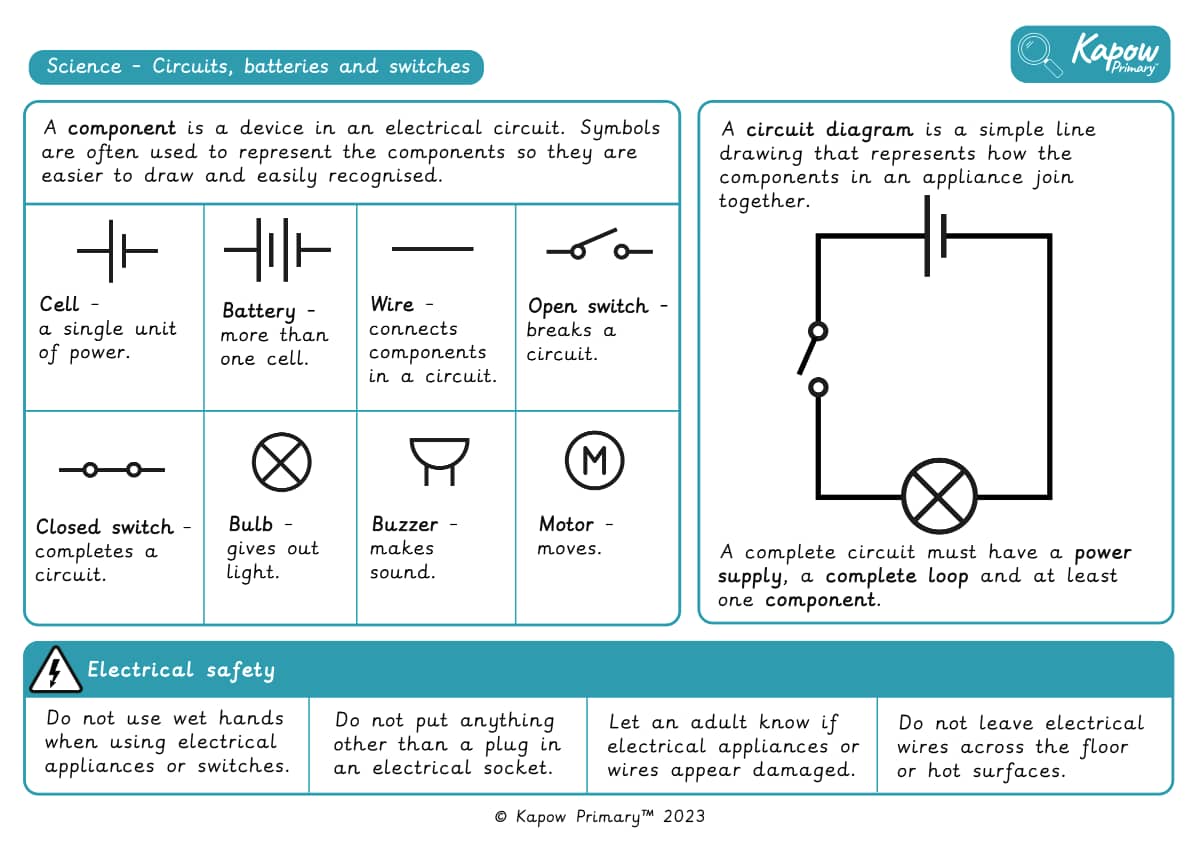
Knowledge organiser – Science Y6: Energy: Circuits, batteries and switches
Aimed at pupils, two pages providing key facts and definitions from the unit 'Circuits, batteries and switches'.
Vocabulary display – Science Y6: Energy: Circuits, batteries and switches
A display version of the vocabulary from the unit 'Circuits, batteries and switches'.
Cross-curricular opportunities
English: Spoken language.
Mathematics: Number – addition, subtraction, multiplication and division; Measurement; Statistics.
Design and technology: Design; Technical knowledge.
British values: Mutual respect; Democracy.

